A) − z i 2 y j x k b) ( z − x )i ( z − 2 y )k c) ( x − z )i 2 x j 2 y k d) y k more_vert Find the curl of F( x , y , z ) = ( x 2 y 2 )i ( xz )j ( yz )kIt is not possible to visualize a 4D plot (the equation in the question will have 4 axis system of 3 independent variables {x,y,z} and 1 dependent variable, {F} ), at least with the technology that we have access to now But it is possible to visuThis tool graphs z = f(x,y) mathematical functions in 3D It is more of a tour than a tool All functions can be set different boundaries for x, y, and z, to maximize your viewing enjoyment This tool looks really great with a very high detail level, but you may find it more comfortable to use less detail if you want to spin the model

Graphs And Level Curves
F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 graph
F x y z x 2 y 2 z 2 graph-Contact Pro Premium Expert Support »Calculus Calculus (MindTap Course List) Describe the level surfaces of the function f ( x , y , z ) = x 2 3 y 2 5 z 2 more_vert Describe the level surfaces of the function f ( x , y , z ) = x 2 3 y 2 5 z 2
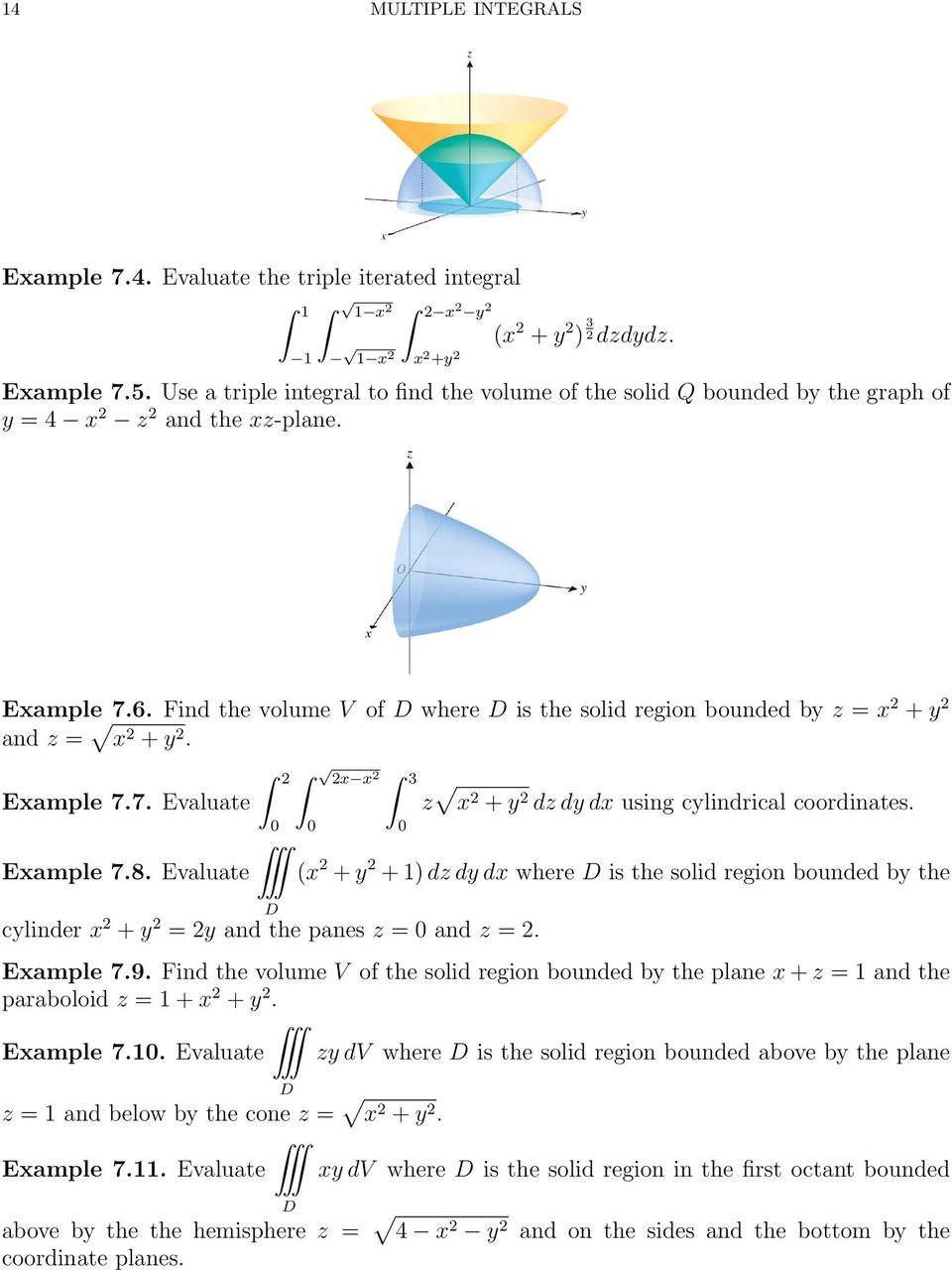


Multiple Integrals H 2 Y Are Continuous Functions On C D And Let F X Y Be A Function Defined On R Then Pdf Free Download
2/23/15 · Hello, Let mathcal(S) the surface of equation z = ln(x^2y^2) it's the graph of your function f Remark that mathcal(S) is a revolution surface, because f(x,y) = g(r) where r = sqrt(x^2y^2) is the polar radius Actually, g(r) = ln(r^2) = 2 ln(r) So, graph the curve of equation z = 2ln(x) in the xOz plane You get Finally, rotate this curve around the Oz axisType Homework Help Uploaded By bunnyyoon Pages 7 This preview shows page 5 7 out of 7 pages11/29/15 · In Mathematica tongue x^2 y^2 = 1 is pronounced as x^2 y^2 == 1 x^2y^2=1 It is a hyperbola, WolframAlpha is verry helpfull for first findings, The Documentation Center (hit F1) is helpfull as well, see Function Visualization, Plot3Dx^2 y^2 == 1, {x, 5, 5}, {y, 5, 5} ContourPlot3Dx^2 y^2 == 1, {x, 5, 5}, {y, 5, 5}, {z, 5, 5}
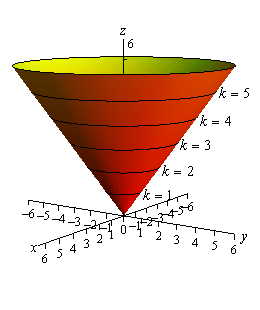
Edit The graph of f has an inflection point at x = 2 The graph of f has a relative maximum at x = 2 Calculus The graph of f ′(x) is continuous and decreasing with an xintercept at x = 0Using the theory of elliptic curves, we study the nontrivial rational (parametric) solutions of the Diophantine equations $z^2=f(x)^2 \\pm f(y)^2$ for some simpleHere the surfaces corresponds to f = 4,8,12,and 16 Example 2 f(x,y,z) = x 2 z 2, the level Surfaces are the concentric cylinders x 2 z 2 = c with the main axis along the y axis With some adjustments of constants these level surfaces could represent the electric field of a line of charge along the y axis Here we have f = 2,4,8,12, and 16
The trace in the x = 1 2 plane is the hyperbola y2 9 z2 4 = 1, shown below For problems 1415, sketch the indicated region 14 The region bounded below by z = p x 2 y and bounded above by z = 2 x2 y2 15 The region bounded below by 2z = x2 y2 and bounded above by z = y 7Plot3D5 Sqrtx^2 y^2, {x, 5, 5}, {y, 5, 5}, RegionFunction > Function{x, y, z}, 0 < z < 5 An essential difference between RegionFunction and PlotRange when using RegionFunction , all points generated outside the region are discarded before building the 3D object to show, and the boundary of the region is computed and plotted nicelyAs long as y>0, the gradients of y=f(x) and y 2 =f(x) have the same sign for a certain x value, and they have stationary points located at the same x values y 2 =f(x) is symmetrical about the xaxis At the x values where y=f(x) passes through the xaxis, provided f'(x)≠0, y 2 =f(x) passes vertically through the xaxis


Graphs Of Surfaces Z F X Y Contour Curves Continuity And Limits



Matlab Tutorial
S is defined as a sphere However, when I type "S f(x,y,z) = 1" into the input bar, nothing is graphed and the algebra window shows S as an undefined Implicit CurveGraph x^2y^2=1 Find the standard form of the hyperbola Tap for more steps Flip the sign on each term of the equation so the term on the right side is positive Simplify each term in the equation in order to set the right side equal to The standard form of an ellipse or hyperbola requires the right side of the equation beThink about how you'd find the domain of a function with one variable, like f(x)=1/x or g(x)=sqrtx The same idea applies, the term under the square root can't be negative, ie 25x 2 y 2 z 2 >=0 1



1 Xyz 2 X Yz 2 Xy Z 2 See How To Solve It At Qanda



Pdf Applications Of Level Curves To Some Problems On Algebraic Surfaces
Question F1(x,y,z) = X^2 y^2 z^2 −1 = 0 F2(x, Y, Z) = 2x^2 Y^2 − 4z = 0 F3(x,y,z) = 3x^2 −4yz^2 = 0 This System Can Be Concisely Represented As F(x) = 0, Where F(x) = (f1, F2, F3)T , X=(x,y,z)T And 0 = (0,0,0)T (transpose Written Because These Should Be Column Vectors) Using Matlab Starting With The Initial Condition X0 = (05, 05, 05)T , ImplementY^2 = x^2 z^2 has the form of an equation for a circle So, you are stacking, in the y direction, circles of increasing radius, one on top of the other Share1/11/02 · For a function of one variable, f, the set of all points (x, y), where y = f(x) is the graph of the function f For a function g of two variables, the set of all points (x, y, z), where z = g(x, y) is the graph of the function g A sketch of the graph of such a function or relation would consist of all the salient parts of the function or



Find And Sketch The Domain Of The Function F X Y Z Ln 16 4x 2 4y 2 Z 2 Youtube



6 1 Functions Of Several Variables Mathematics Libretexts
Graphs Solve Equations Surface integrals Find the area of the portion of the cone x^2y^2=z^2 above the xy plane and inside the cylinder x^2y^2=ax Surface integrals Find the area of the portion of the cone x 2 y 2 = z 2 above the x y plane and inside the cylinder x 2 y 2 = a x10/4/17 · 设f(xyz)=xyz,gradf(211)= 设函数f(x,y)=5-跟号下x方加y方,求gradf(2,1) (1)设f(x,y,z)=x^22y^23z^2xy3x2y6z,则gradf(1,1,1)=(2)已知z=x^2y^3,则a^2 z/ax^2= 求答案 谢 求函数f = ln(x² y² z²)在点M(1,2,2)处的梯度gradfM 设f(x)=1/x若f(x)f(y)=f(z),求zLet f(x) be a differentiable function satisfying f (x y) = f (x) f (y) ∀ x, y ∈ R and f (0) = 1 then x → 0 lim x 3 f (sin x) 2 f (t a n 2 x) − 2 f (s i n 2 x) equals to?


Calculus Iii Lagrange Multipliers


Surface Area
Add to graph Function z=f(x,y) Space Curve r(t) Vector Field Point (x, y, z) Vector Text Label Implicit Surface Parametric Surface Region Slider ────────── Function r=f(θ,z) Function z=f(r,θ) Function ρ=f(θ,φ) Function x=f(y,z) Function y=f(x,zHow can i draw graph of z^2=x^2y^2 on matlab Learn more about surface MATLAB C/C Graphics LibraryLet {eq}f(x,y,z)=x^2y^2z^2 {/eq} and let S be the level surface defined by f(x,y,z) = 4 (a) Find an equation for the plane tangent to S at {eq}P_{0}(1,1,2)



Webwork Exam Review Solutions


Mathematics Calculus Iii
A quick video about graphing 3d for those who never done it before Pause the video and try itLet S be the surface of equation z = \text{arcsin}(x^2y^22) S is a surface of revolution because z = F(r) where r=sqrt{x^2y^2} Here, F(r) = \text{arcsin}(r^22) First, you study the curve of equation z = \text{arcsin}(x^22) you get Second, you rotate this curve around (0z) axis and you get the surface S Remark that f exists only on the domain defined by 1\leqCompute answers using Wolfram's breakthrough technology & knowledgebase, relied on by millions of students & professionals For math, science, nutrition, history



Solved Finding An Equation Of A Tangent Plane In Exercise Chegg Com



Graphing 3d Graphing X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Intro To Graphing 3d Youtube
12/2/15 · macias (ygm97) – Homework 13 – staron – () 17 Consequently, volume = 2 π 1 − 5 e 4 cu ft/hour 026 100 points The solid shown in lies below the graph of z = f (x, y) = 3 x 2 − y 2 above the disk x 2 y 2 ≤ 1 in the xyplane Determine the volume of this solid 11 Verified Answer View Answer2/12/17 · how can i draw graph of z^2=x^2y^2 on matlab Follow 309 views (last 30 days) Show older comments Rabia Kanwal on 12 Feb 17 Vote 0 ⋮ Vote 0 Commented Walter Roberson on 10 Mar Accepted Answer Star Strider 0 Comments Show Hide 1 older comments Sign in to comment Sign in to answer this question



Multiple Integrals H 2 Y Are Continuous Functions On C D And Let F X Y Be A Function Defined On R Then Pdf Free Download



Calculate The Double Integral Over S Of F X Y Z Ds For Y 7 Z 2 0 Less Than Or Equal To X Less Than Or Equal To 7 0 Less
Series x^2 y^2 z^2 f(x, y, z) show histogram of image image of x^2 y^2 z^2 f(x, y, z) Have a question about using WolframAlpha?Graph x=4y^2 Reorder and Find the properties of the given parabola Tap for more steps Rewrite the equation in vertex form Tap for more steps Complete the square for Tap for more steps Use the form , to find the values of , , and Consider the vertex form of a parabolaCurves in R2 Graphs vs Level Sets Graphs (y= f(x)) The graph of f R !R is f(x;y) 2R2 jy= f(x)g Example When we say \the curve y= x2," we really mean \The graph of the function f(x) = x2"That is, we mean the set f(x;y) 2R2 jy= x2g Level Sets (F(x;y) = c) The level set of F R2!R at height cis f(x;y) 2R2 jF(x;y) = cg Example When we say \the curve x 2 y = 1," we really mean \The



If X Y Z 0 Then Prove That X 2 Yz Y 2 Zx Z 2 Xy 3 Brainly In



X 2 Y 2 Z 2 4 Graph Novocom Top
4/28/17 · \ \underbrace{f(x,y,z)=x^2−2xyy^23yz−z^24x−2y3x−6}_{\text{a polynomial in three variables}}\ and \g(x,y,t)=(x^2−4xyy^2)\sin t−(3x5y)\cos t\ In the first function, \((x,y,z)\) represents a point in space, and the function \(f\) maps each point in space to a fourth quantity, such as temperature or wind speed2/12/17 · how can i draw graph of z^2=x^2y^2 on matlab Follow 270 views (last 30 days) Show older comments Rabia Kanwal on 12 Feb 17 Vote 0 ⋮ Vote 0 Commented Walter Roberson on 10 Mar Accepted Answer Star Strider 0 Comments Show Hide 1 older comments Sign in to comment Sign in to answer this questionGraph of a hyperbolic paraboloid The graph of the function $f(x,y)=x^2y^2$ More information about applet Example 2 Let $f(x,y,z) = x^2y^2z^2$



How Do I Reproduce This Heart Shaped Mesh In Matlab Stack Overflow
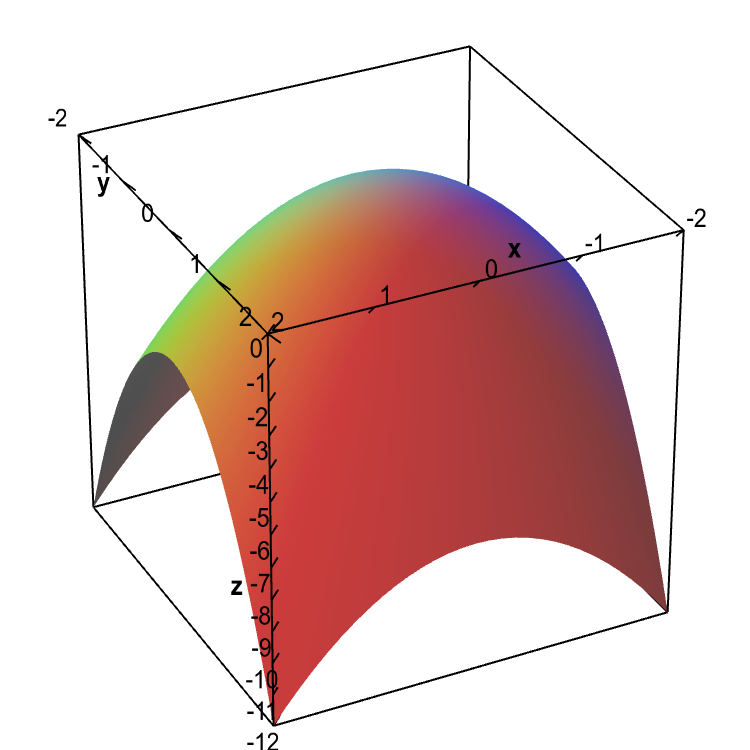


Level Sets Math Insight
3/31/16 · 设z=f(x^2y^2),其中f具有二阶导数,求 ∂z^2/ ∂x^2, ∂z^2/ ∂x ∂y, ∂z^2/ ∂y^2(高等数学) 展开 我来答 可选中1个或多个下面的关键词,搜索相关资料。When I type "S x^2 y^2 z^2 = 1" into the input bar, this works perfectly;The graph of f ′(x) is continuous and decreasing with an xintercept at x = 2 Which of the following statements must be true?



Calc 501 1000 By James Bardo Issuu



Graphs And Level Curves
Graphs Solve Equations We have x^2y^2=36z^2 and xy=10z, which gives (10z)^22xy=36z^2 or xy=3210zz^2 and xyz=32z10z^2z^3 Also, (xy)^2\geq4xy, which gives 3z^2z28\leq0 or 2\leq z\leq\frac{14}{3} We have x 2 y 2 = 3 6 · The equation ##x^2 y^2 = 0## can be thought of as a degenerate circle whose center is at (0, 0) and whose radius is 0 In other words, the point (0, 0) The graph of the solution set of the inequality ##x^2 y^2 > 0## is all of the points2/15/16 · 3Dplot of "x^2y^2z^2=1" Learn more about isosurface;
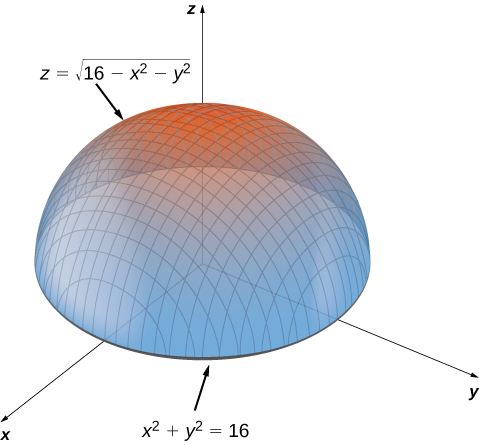


Maxima Minima Problems Calculus Volume 3
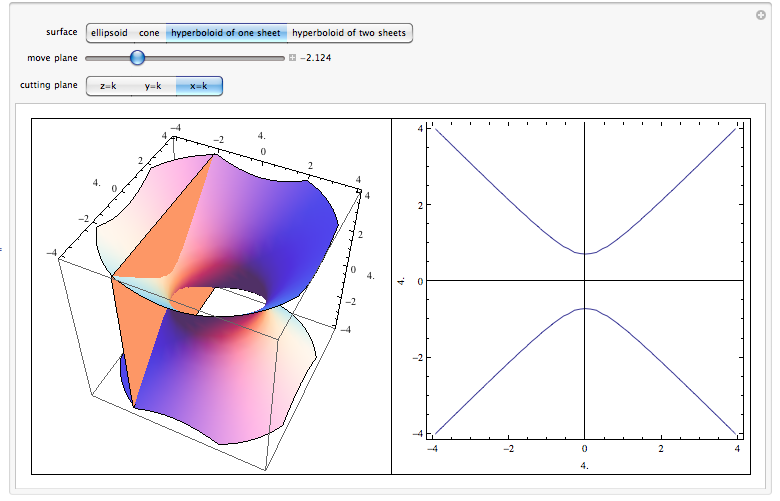


Level Surfaces
Minimize the function f(x, y, z)=x^{2}y^{2}z^{2} subject to the constraints x2 y3 z=6 and x3 y9 z=9 Video Transcript So the question is gonna look a little bit different We instead of having one constraints, we're gonna find extreme valueHere is a picture of the saddle z=x^2y^2 cut with plane y=0 or cut with plane x=0 Similarly, the saddlez=2xy cut with plane x=y or cut with plane x=y Actually these graphs z=x^2y^2 and z=2xy (over the whole plane) have exactly the same shape since rotation around the zaxis by 45 degrees takes one graph into the otherCourse Title CALCULUS 408;
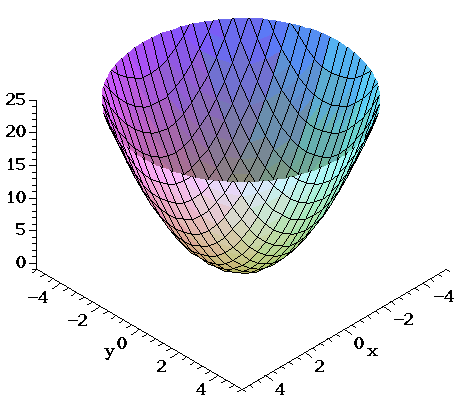


Surfaces Part 2
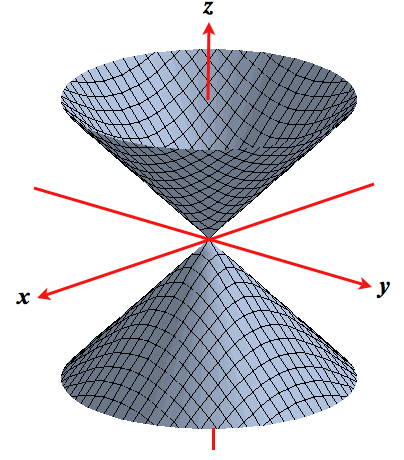


Level Surfaces
The trace of the graph of z f x y x 2 2 y 2 on the plane z 2 is which of the The trace of the graph of z f x y x 2 2 y 2 on the School University of Texas;3dprinting, solidworks f(0,0,0) is 0, not 1 (the isosurface level), so you only get points drawn completing the cones if there are enough points near the origin that happen to have value 1 But when you switch to linspace(,,), the closest coordinates to the origin are at about 105, leaving a gap of about 21For the function f (x, y, z) = 3 x − 4 y 2 z 9 − x 2 − y 2 − z 2 f (x, y, z) = 3 x − 4 y 2 z 9 − x 2 − y 2 − z 2 to be defined (and be a real value), two conditions must hold The denominator cannot be zero The radicand cannot be negative Combining these conditions leads to the inequality



Level Surfaces In Matlab



2 3 Tangent Plane To A Surface Mathematics Libretexts
The graph of a function f(x;y) = 8 x2 y) So, one surface we could use is the part of the surface So, one surface we could use is the part of the surface z= 8 x 2 yinside the cylinder x 2 y11/24/19 · Verify Stokes theorem for F =(y^2 z^2 x^2)i (z^2 x^2 y^2)j (x^2 y^2 z^2)k over the portion of the surface x^2 y^2 2ax az = 0 Let g be the function that represents the area under the graph of f between 0 and x (a) Use geometry to find a formula for g(x) (b) Verify that g is an antiderivative of f and explain how this


How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic


Calculus Iii Functions Of Several Variables



Multidimensional Graphs Article Khan Academy
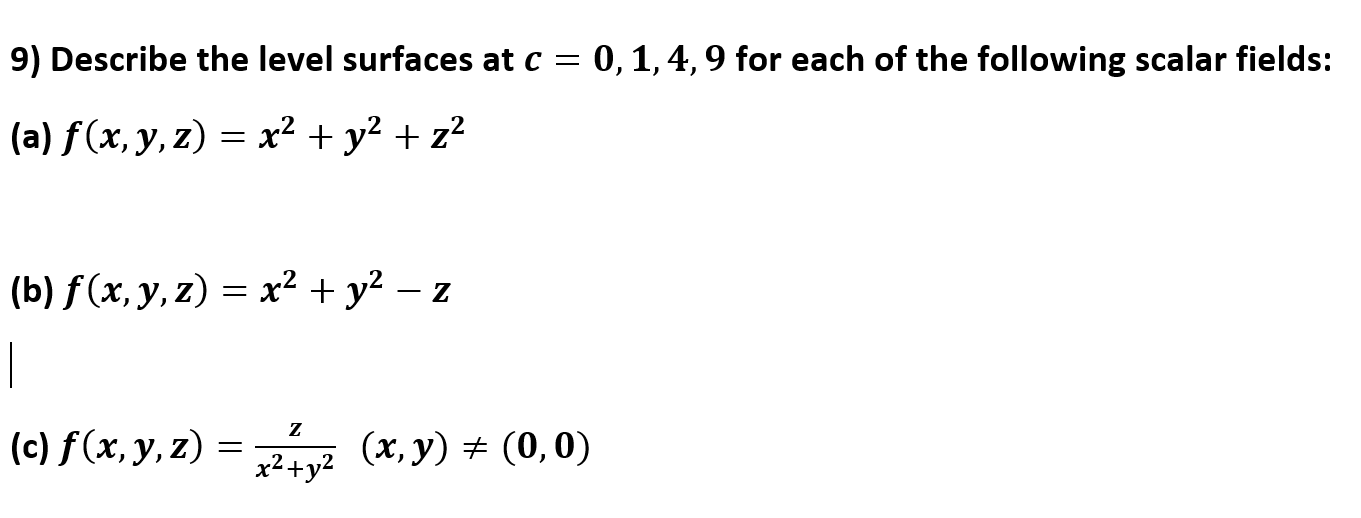


Answered 9 Describe The Level Surfaces At C Bartleby



Answered 9 M A Y Z Xyz Xyz P 2 1 1 U Bartleby


How To Construct The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 9 Quora


Gnu Octave Three Dimensional Plots


Plotting Www Scilab Org


Level Surfaces Nb


Surfaces Part 2



F X Y X 2 Y Y Y F F X X 2xyx 2 3y Y Ln2 Z F X Y Cos Xy X Cos 2


Visualizing Functions Of Several Variables And Surfaces



How To Plot 3d Graph For X 2 Y 2 1 Mathematica Stack Exchange
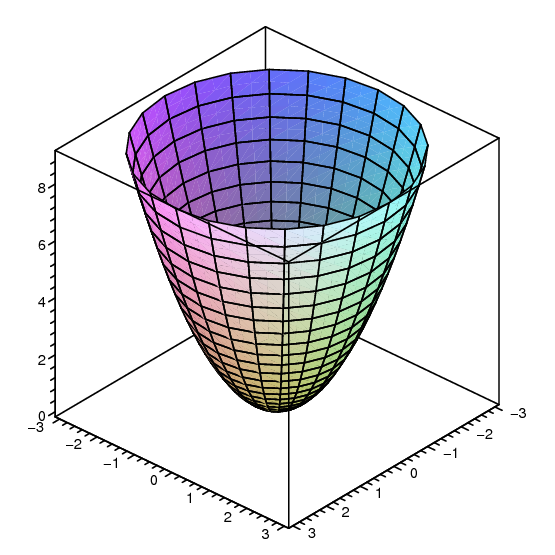


14 1 Functions Of Several Variables
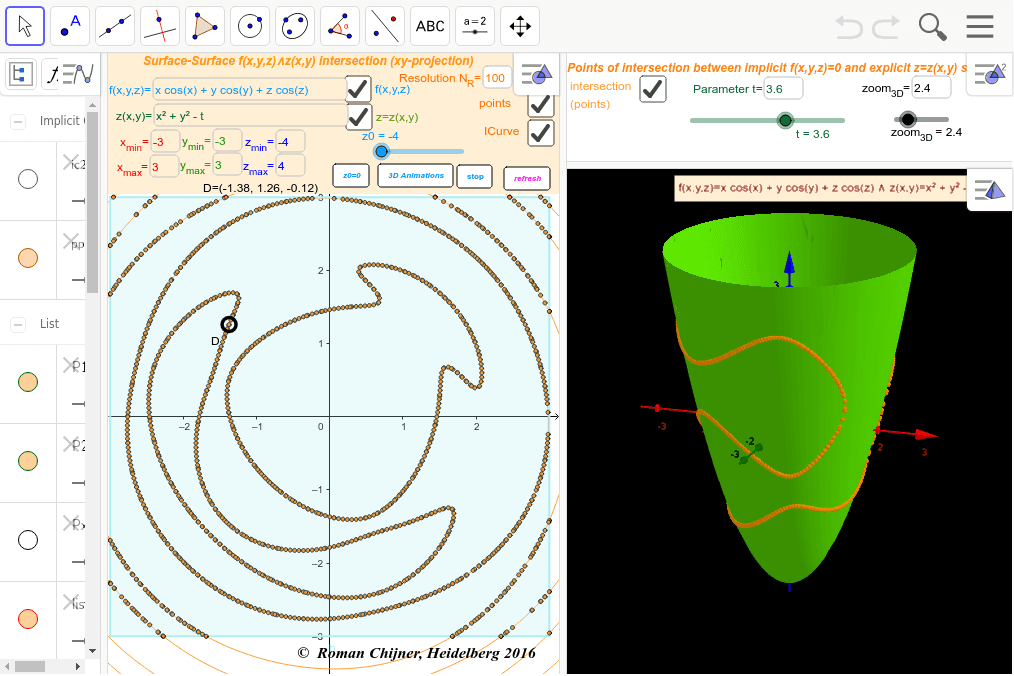


Points Of Intersection Between Implicit F X Y Z 0 And Explicit Z Z X Y Surfaces Geogebra



How Do I Reproduce This Heart Shaped Mesh In Matlab Stack Overflow



How To Plot X 2 Y 2 Z 2 Mathematics Stack Exchange
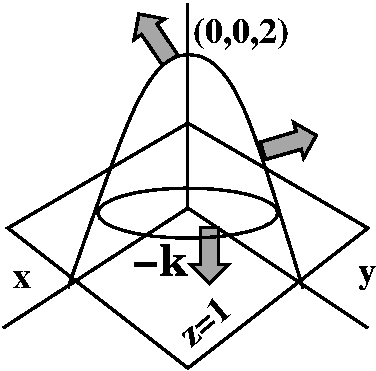


Math 251 Diary Spring 06
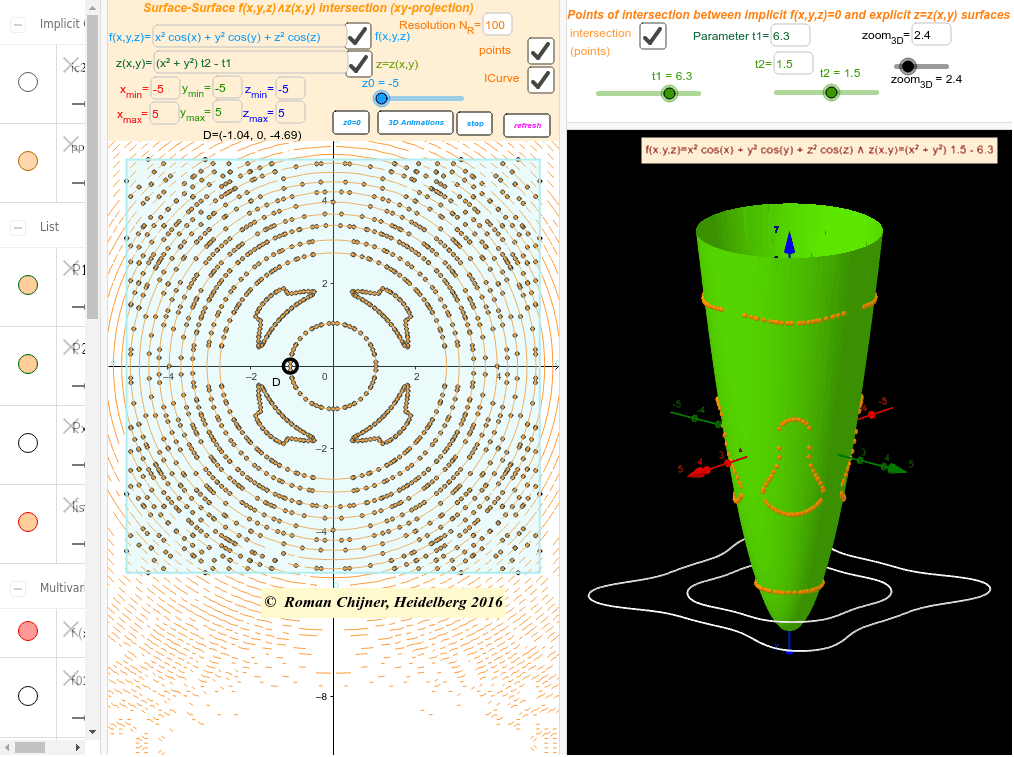


Points Of Intersection Between Implicit F X Y Z 0 And Explicit Z Z X Y Surfaces Geogebra
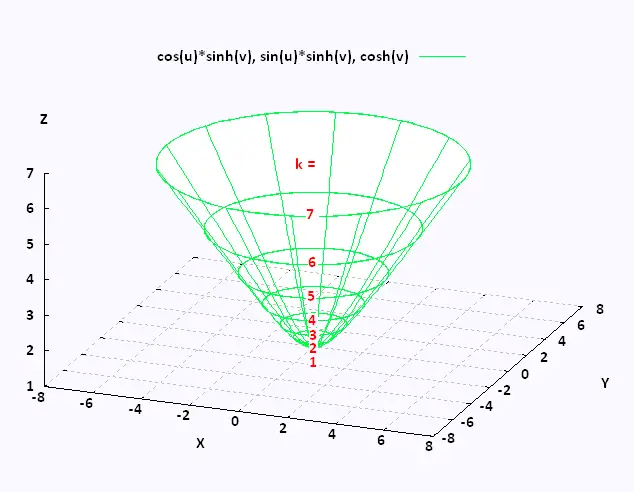


Mathematics Calculus Iii


Sketching Surfaces In 3d


Surface Area



Matlab Tutorial
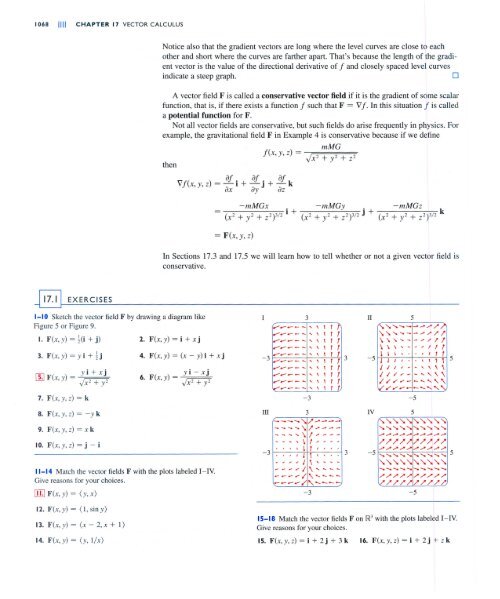


F X Y Z


Deep Neural Networks As Computational Graphs By Tyler Elliot Bettilyon Teb S Lab Medium
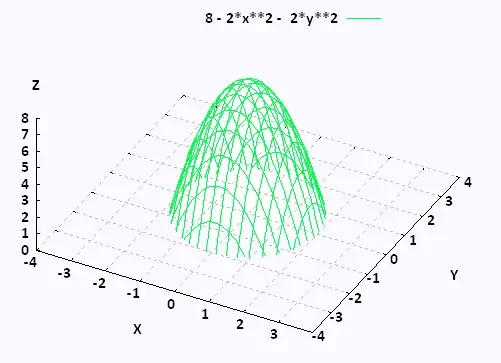


Mathematics Calculus Iii



Saddle Point Wikipedia
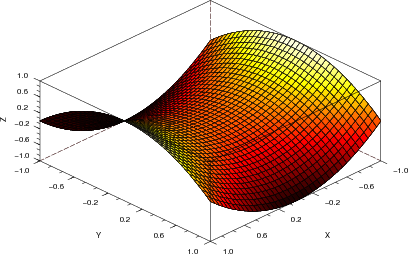


Realiser Des Graphiques Avec Scilab



If X 2 Y 2 Z 2 R 2 And X Y Z 0 Then Tan 1 Xy Z



Lagrange Multipliers



How Do I Graph Z Sqrt X 2 Y 2 1 Without Using Graphing Devices Mathematics Stack Exchange



Multivariable Calculus F X Y X Ln Y 2 X Is A Function Of Multiple Variables It S Domain Is A Region In The Xy Plane Ppt Download



Sketch The Graph Of F X Y Sqrt 1 X 2 Y 2 State The Domain And Range Of The Function Study Com
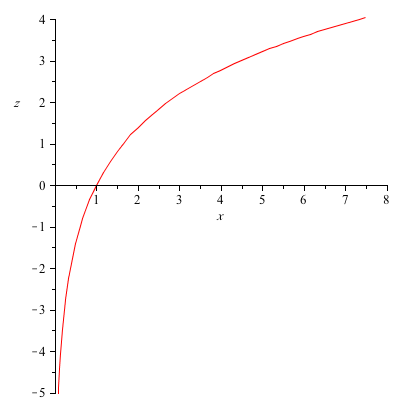


How Do You Sketch F X Y Ln X 2 Y 2 Socratic



Notes Up To Ch7 Sec3
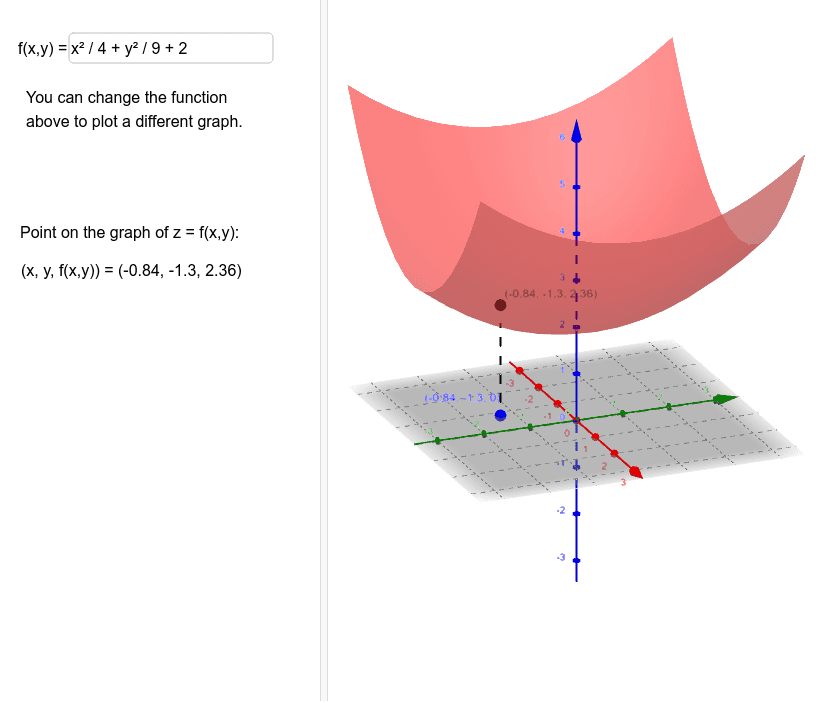


Graph Of Z F X Y Geogebra


Xyz 3 D Mesh Surface Plotter
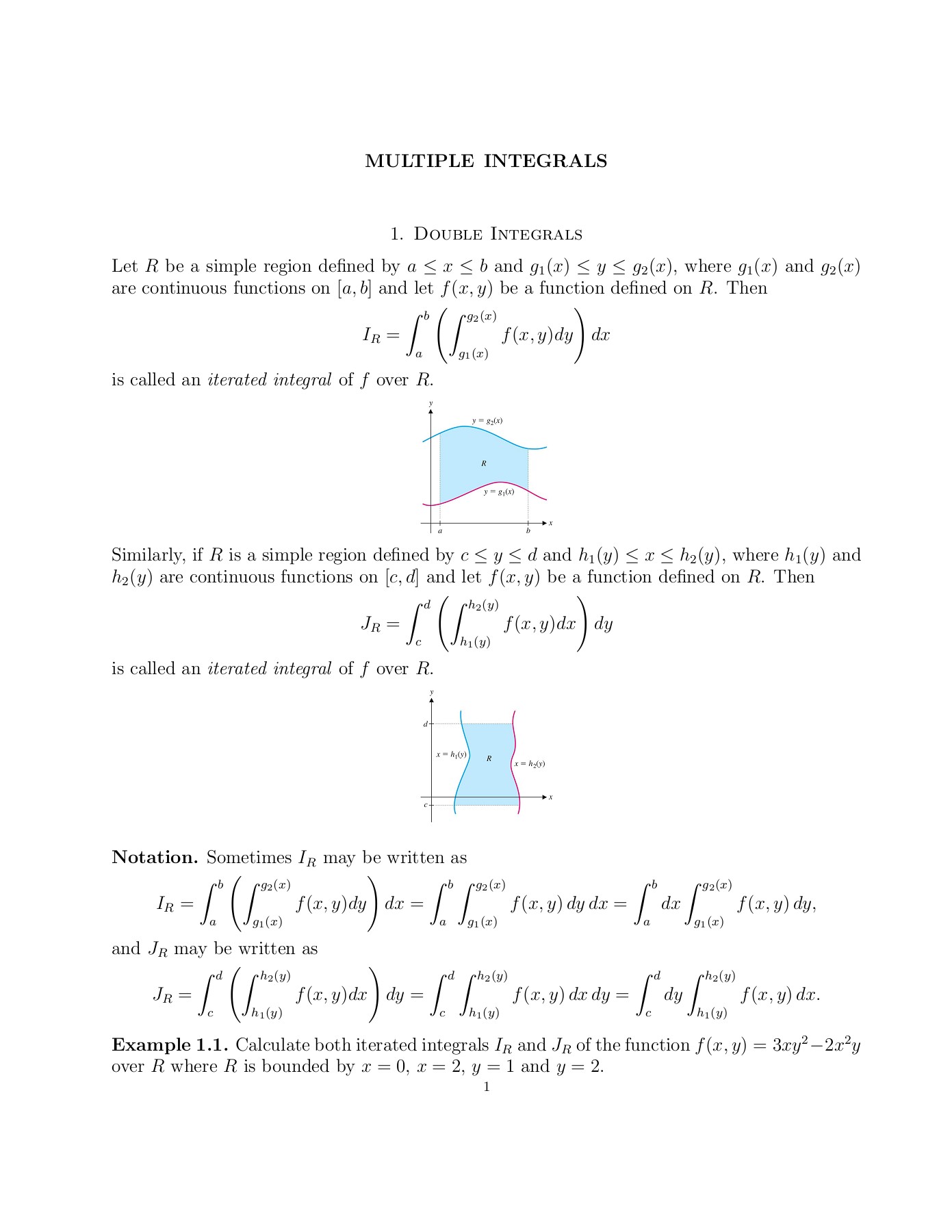


1 Double Integrals Cankaya Universitesi Flip Ebook Pages 1 16 Anyflip Anyflip


Mesh Surface Plot Matlab Mesh



Level Surfaces In Matlab



Functions Of Several Variables Calculus



Assignment Previewer Department Of Mathematics Ccny Pages 1 22 Flip Pdf Download Fliphtml5
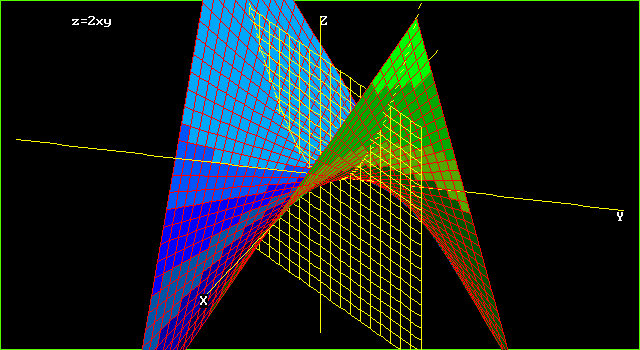


Graphs Of Surfaces Z F X Y Contour Curves Continuity And Limits
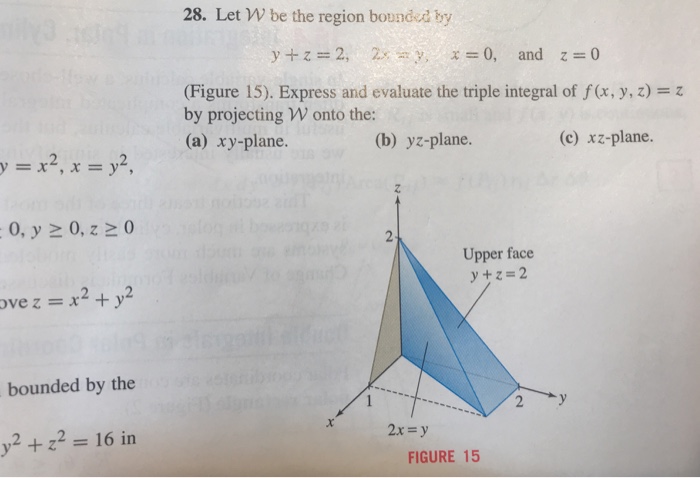


Solved 28 Let W Be The Region Bounded By Y Z 2 2x Y X Chegg Com
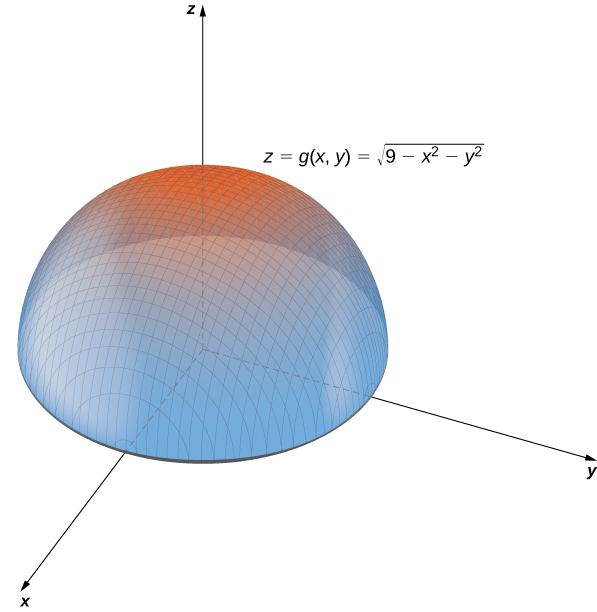


Graphing Functions Of Two Variables By Openstax Jobilize
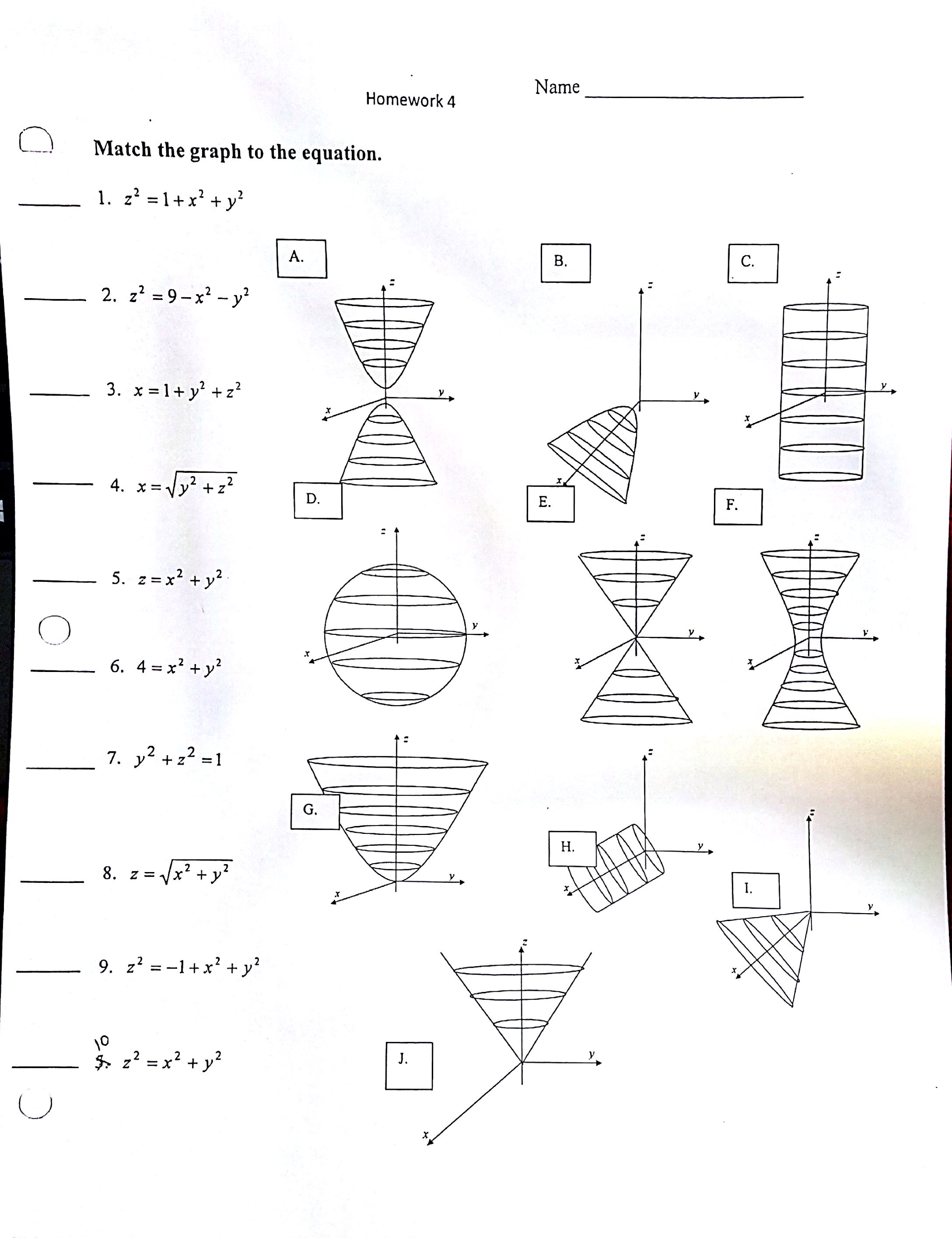


Solved Match The Graph To The Equation X 2 1 X 2 Y Chegg Com



Level Surfaces
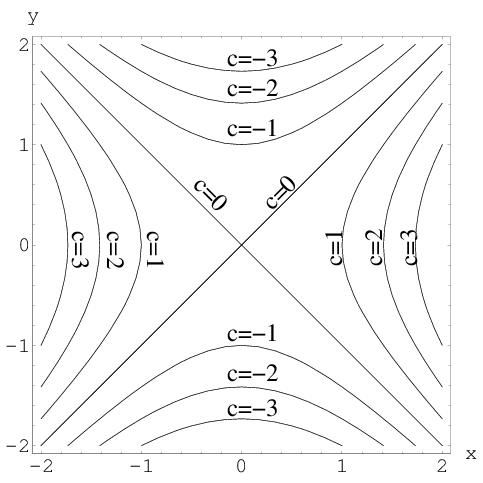


Level Set Examples Math Insight
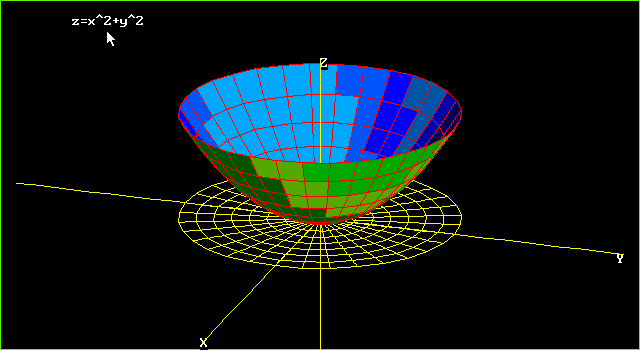


Graphs Of Surfaces Z F X Y Contour Curves Continuity And Limits
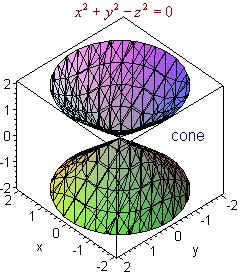


Surfaces



Get Answer Suppose F X Y Z X2 Y2 Z2 And W Is The Solid Cylinder With Height Transtutors



Factorising Cyclic Expression X 2 Y Z Y 2 Z X Z 2 X Y Youtube
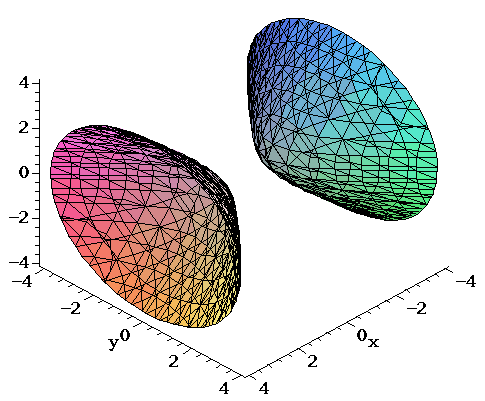


Surfaces Part 2



Quadratic Function Wikipedia


What Is The Graph Of X 2 Y 2 Z 2 1 Quora



Notes Up To Ch7 Sec3



The Graph Of The X Y Z 0 Plane Download Scientific Diagram



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿